The Importance of ESG Transparency and Reporting: Driving Sustainability through Accountability
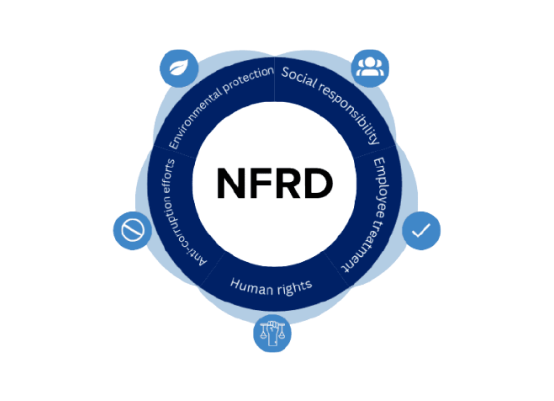
As businesses navigate an increasingly complex and interconnected world, the significance of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors cannot be overlooked. ESG transparency and reporting have emerged as powerful tools to assess, communicate, and improve a company’s sustainability performance.
We explore below the importance of ESG transparency and reporting, highlighting the benefits it brings to businesses, investors, and society at large.